
Vitamin K2-7, Methylcobalamin, Cholecalciferol & Calcium Citrate Tablet
Product Details:
- Purity 97%
- Formulations Type General Drugs
- Formulations Form Tablets
- Gender/Age Group Adult
- Storage Instructions Store in Cool
- Click to view more
Vitamin K2-7, Methylcobalamin, Cholecalciferol & Calcium Citrate Tablet Price And Quantity
- 67 INR/Box
- 300 Box
Vitamin K2-7, Methylcobalamin, Cholecalciferol & Calcium Citrate Tablet Product Specifications
- Tablets
- Store in Cool
- 97%
- General Drugs
- Adult
Vitamin K2-7, Methylcobalamin, Cholecalciferol & Calcium Citrate Tablet Trade Information
- Cash Advance (CA) Cash in Advance (CID)
- 300 Box Per Month
- 1 Months
- Yes
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Western Europe Australia Eastern Europe Central America Middle East South America Asia North America Africa
- All India
Product Description
This combination is useful in people having low blood calcium levels; who do not get enough calcium from their diets. Calcium is necessary for many normal functions of body, especially bone formation and maintenance. Low blood levels of calcium may cause bone disease. Thus this combination helps in maintance of calcium & healthy bones.
Calcium Citrate is calcium salt of citric acid. Calcium salt can be used in the prevention of calcium deficiency states. It is also used as an adjunct in the prevention of osteoporosis.
Methylcobalamin is the neurologically active form of the vitamin B12 and has strong effect on the brain and nervous system being also very important for cell growth and production. Methylcobalamin is used in variety of processes, including: production of red and white blood cell, the regeneration of RNA and DNA, synthesis of proteins. It is useful in vitamin B12 deficiency, psoriasis, pernicious anemia & atopic dermatitis.
Cholecalciferol is a fat soluble vitamin D3. Vitamin D is important for the absorption of calcium and phosphorus. Having the right amount of vitamin D, calcium, and phosphorus is important for building and keeping strong bones.
Vitamin K2-7 shown to have significant importance for optimal utilization of calcium in the body related to bone and cardiovascular health. Daily supplementation is expected to be beneficial for the bone building process as well as for cardiovascular health. Different forms of vitamin K2 are well documented and shown to be safe in numerous humans studies.
Indication:

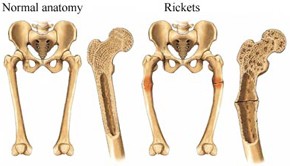 â— Beneficial in osteoporosis
â— Beneficial in osteoporosis
â— Beneficial in rickets (softening and weakening of the bones in children due to deficiency of vitamin D)
â— Beneficial in osteomalacia (softening and weakening of bones in adults caused by lack of vitamin D)
â— Maintain calcium level in body
â— Beneficial in bone health
â— Maintain integrity of the bones
Pharmacology:
Calcium citrate: All of the calcium salts act as dietary supplements to prevent or treat negative calcium balance. Calcium citrate contains 21% elemental calcium.Absorption from the GI tract requires Vitamin D. Available elemental calcium depends on the salt form used, dose administered and the presence of an acid environment in the stomach. Elimination is primarily in the feces as unabsorbed calcium and the kidneys eliminate 20%.
Methylcobalamin: Mecobalamin is the neurologically active form of vitamin B12 and occurs as a water-soluble vitamin in the body. It is a cofactor in the enzyme methionine synthase, which functions to transfer methyl groups for the regeneration of methionine from homocysteine. By depleting excess homocystine, folate benefits cardiovascular health and nervous system function.
Cholecalciferol: Cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) is formed in the skin following exposure to ultraviolet light and it is taken in through food (e.g. fatty fish, dairy products). The vitamin is tranformed into active 1.25-dihydroxycholecalciferol (1.25(OH)2D3, calcitriol) in two hydroxylation steps, first in the liver, then in the kidneys. Calcitriol is a highly efficient steroid hormone. It regulates the metabolism of calcium and phospahtes by stimulating their intestinal absorption, the mobilisation from the bones, and the renal reabsorption of calcium.
Vitamin K2-7: Vitamin K2 is further of two types; The two subtypes most studied are menaquinone-4 (menatetrenone, MK-4) and menaquinone-7 (MK-7). Menaquinone-7 (MK-7) is different from MK-4 in that it is not produced by human tissue. MK-7 consumption has been shown to reduce the risk of bone fractures and cardiovascular disorders that are crucial health issues worldwide.
Drug Interactions:
â— Warfarin (Coumadin) interacts with VITAMIN K.
â— Vitamin K is used by the body to help blood clot. Warfarin (Coumadin) is used to slow blood clotting. By helping the blood clot, vitamin K might decrease the effectiveness of warfarin (Coumadin). Be sure to have your blood checked regularly. The dose of your warfarin (Coumadin) might need to be changed.
â— Calcium citrate can decrease the absorption of other drugs such as bisphosphonates (e.g.,alendronate), tetracycline antibiotics (e.g., doxycycline, minocycline), estramustine, levothyroxine, and quinolone antibiotics (e.g., ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin).
Side Effects:
â— Weakness
â— Headache
â— Somnolence
â— Nausea
â— Vomiting
â— Dry Mouth
â— Constipation
Contraindications:
This combination should not be given to patients with hypercalcaemia and to those with the evidence of vitamin D toxicity and should not be given to anyone who is hypersensitive to any ingredient.

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+







